Science : Food and Health (Class V)
Q. Define diet.
Ans: The food we eat daily is called our diet.
Q. Define balance diet.
Ans: A balanced diet gives your body the nutrients it needs to function correctly.
CARBOHYDRATES:
◾It gives us energy to work and play.
◾ Cereals, potatoes, sugar, bread, etc contain carbohydrates.
◾ It is also known as energy-giving food.
FATS:
◾It is the source of stored energy in our body.
◾It gives us energy more than carbohydrates.
◾Butter, ghee, oil, etc contain fats.
◾ It is also known as energy-giving food.
PROTEINS:
◾These are essential for growing children.
◾Milk, egg, meat, peas and fish contain protein.
◾They are also known as body-building food.
VITAMINS & MINERALS:
◾Vitamins kerp us fit and help us to fight diseases.
◾Minerals help us in the growth and development of body.
◾They both are known as protective food.
ROUGHAGE:
◾ It means fibre which is present in fruits and vegetables.
◾It helps our body to get rid of undigested food.
Q. Why should we never wash vegetables after peeling and cutting?
Ans: Never wash vegetables after peeling and cutting:
◾It washes away many vitamins and minerals.
◾A lot of starch (carbohydrates) is thrown out with the water in which rice is cooked.
Q. How does regular exercise help us?
Ans: It is very important for good health because:
◾It helps to keep the muscles in good tone.
◾It helps to keep the bone strong.
◾It helps the nervous system by supplying extra blood to the brain.
◾ It hrlps the lungs, heart and blood vessels to work well.
Q. How does regular sleep help us?
Ans:
◾It recovers cells of the body from the work.
◾It increases our efficiency and strength to work.
◾It build up supplies of energy for the next period of time.
◾It relaxes our muscles.
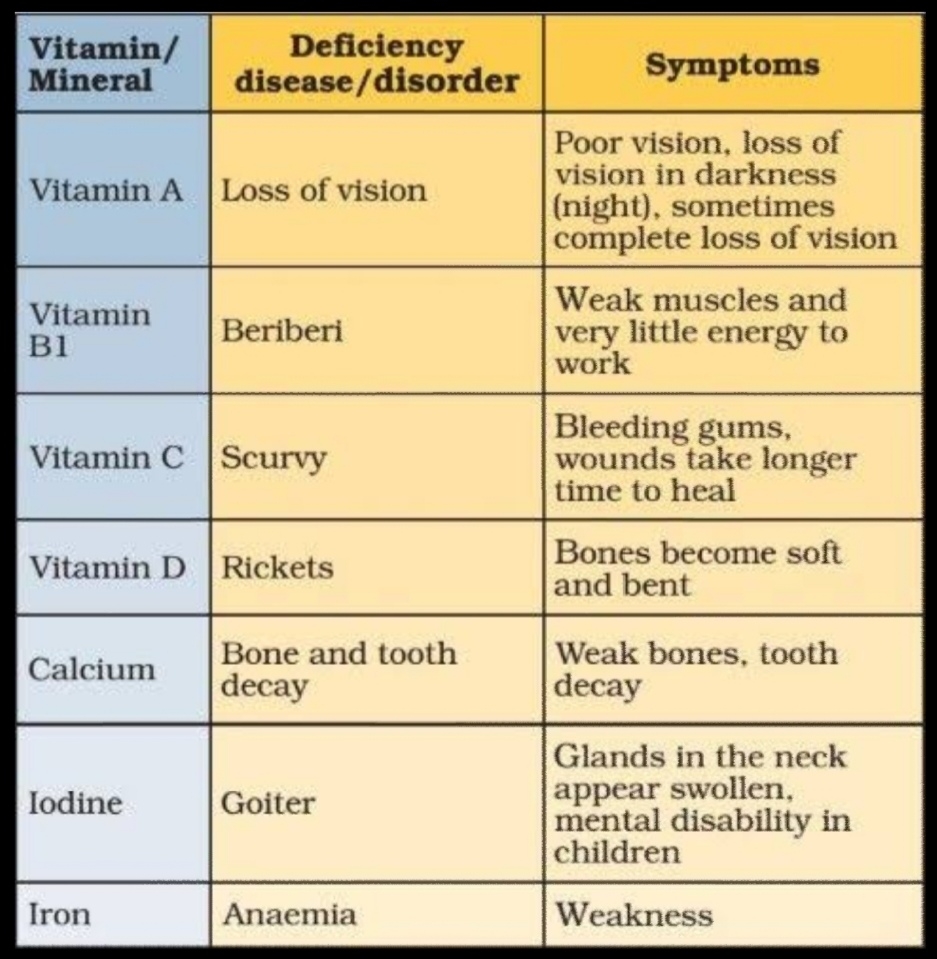
⬆️Above are the non-communicable diseases.
Q. Define Non-communicable diseases.
Ans: Diseases that don not spread from one person to another are called non-communicable diseases.
e.g. Rickets, Scurvy, etc.
Q. Define anaemia.
Ans:
◾ Anaemia is the disease caused by the deficiency of blood in the body.
◾This deficiency is caused by lack of iron in the food.
Q. Define communicble diseases / infectious diseases.
Ans: Diseases that spread from one person to another are called communicble diseases.
e.g. COVID-19, Malaria, Ringworm, Typhoid, etc.
Q. Define micro-organisms.
Ans: Communicable diseases are caused by tiny living things called microbes or micro-organisms.
BACTERIA:
◾Tiny organisms having different shapes.
◾Diseases like meningitis, typhoid and cholera are caused by bacteria.
PROTOZOA:
◾Single - celled micro-organisms.
◾Diseases like malaria and amoeba dysdntery.
VIRUSES:
◾These are smallest micro-organisms.
◾Diseases like COVID-19, common cold, influenza, rabies and measles.
SPREAD OF MICRO-ORGANISMS:
1. Through direct contact
◾Diseases spread by contact are chicken-pox, smallpox, scarlet fever, scabies and ringworm.
2. Through air
◾Diseases spread through air are common cold, flu, pneumonia, tuberculosis, mumps and measles.
3. Through food and water
◾Diseases spread through food and water are cholera, typhoid, food poisoning and dysdntery.
4. Through insects
◾Malaria, dengue, filariasis and yellow fever are carried by mosquitoes.
◾Typhus fever is carried by lice.
◾Plague is carried by fleas that live on rats.
Q. How can we prevent Communicable Diseases?
Ans: These diseases can be controlled by taking following steps:
◾The patient should be kept absolutely isolated.
◾The infected articles like clothes, towel and utensils should be kept separate and disinfected.
◾ Drinking water should be boiled to kill germs.
◾Don not eat cut fruits, they may carry germs.
◾All food articles should be properly covered.
◾ Wash fruits and vegetables before eating.
◾Wash your hand before eat anything.
◾Vaccination should be taken at a proper time.
VACCINATION:
◾Vaccination is the process to protect people especially children fromby acquiring immunity against certain diseases.
◾Many diseases such as measles, typhoid, tetanus, polio and mumps can be controlled through vaccines.
Who discovered vaccination?
Ans: Vaccination was discovered by Edward Jenner.
#rainbowz



Comments
Post a Comment